What Is a Lethal Level of Electrical Voltage
CTBEB.MS.ID.556018
Short Communication
Median Lethal Dose (Ld50) Of Electric Current
Department of Veterinary Pharmacology and Toxicology, Federal University of Agriculture, Nigeria
Submission: October 14, 2019; Published: November 06, 2019
*Corresponding author: Saganuwan Alhaji Saganuwan, Department of Veterinary Pharmacology and Toxicology, College of Veterinary Medicine, Federal University of Agriculture, P.M.B. 2373, Makurdi, Benue State, Nigeria
How to cite this article: Saganuwan Alhaji Saganuwan. Median Lethal Dose (Ld50) Of Electric Current. Curr Trends Biomedical Eng & Biosci. 2019; 19(4): 556018.. DOI: 10.19080/CTBEB.2019.19.556018
Abstract
Electric current constitutes potential hazards across the globe. In view of this, literatures were assessed for determination of lethal dose of electric current that would kill 50% of human (LD50), using cardiorespiratory pathological signs. The low LD50 value of electric current (36.5±21.3mA) and voltage (11.0±6.4 V) respectively, suggest very serious toxicity. The vital toxicity signs were paralysis of respiratory muscle and ventricular fibrillation. Hence, electric current should be avoided since it is severely hazardous.
Keywords: Thunder; Lightning; Lethal dose; Treatment
Introduction
Electrical related deaths are more frequent among school age children as a result of high voltage and lightning strike [1]. Lightening, a transfer of an electrical charge, which results in discharge of static electricity, kills about 1000 people in the US every year [2]. Lightening causes muscular spasm, neurosis, thrombosis, damage of blood vessels, unconsciousness, cardiac arrest, hypoxia, respiratory arrest and death [3]. The types of lightning strikes are intracloud, cloud - to - ground and ground to cloud [4]. The most important resistor to the flow of current from lightening electricity is skin [5]. Estimated are 50,000 thunderstorms, 8 million lightning flashes [6], with mortality rate of 30% [7] and survival rate of 70% [8], affecting more people of less than 40years of age [9]. The effect depends on the intensity of current, voltage, body exposure among others [10]. A voltage of 30V can cause ventricular fibrillation. Electric shock is a sudden violent response to electric current, which may lead to death (electrocution). Let go phenomenon for high voltage (7600V) could be tolerated for 100 milliseconds or less [11]. Lightning has been considered by some ethnic groups as myth, miracle and mirage [12], which is cruelty to animals, and may be caused by witches [13]. In view of traditional beliefs and toxicity effects associated with lightning and electric current, there is need for acute toxicity study of electric current, with a view to determining the resistance threshold of lightning and electric current in humans and animals.
Materials and Methods
Ohm's law states that current is equal to voltage over resistance. A mechanism of death in electric shock drowning as re ported by Fish and Geddes [17] was used to determine the LD50 of lightening current and voltage [14-19]. Arithmetical method of up-and-down procedure was adopted for calculation of LD50 [16].
Results and Discussion
The results of median lethal dose for lightening current, voltage and resistance are presented in Table 1.
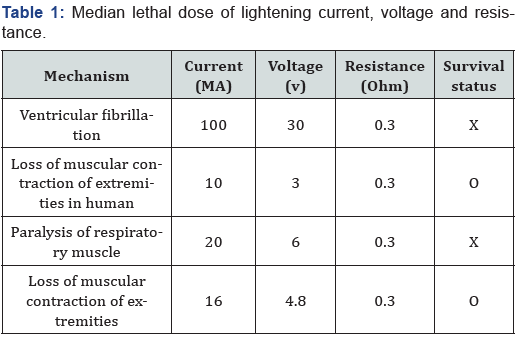
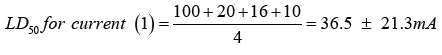
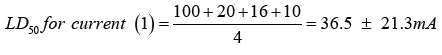
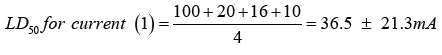
Estimated LD50 for current (36.5 ± 21.3mA) and voltage (11.0 ± 6.4 V) show that electric current is very toxic indicating that 100 mA can cause ventricular fibrillation, 20mA (respiratory muscle paralysis), 16mA and 10mA contraction of extremities [14,15]. More so, 606 electrical injuries and 21 deaths caused by greater than 1000 volts have been reported in Canada [1]. But the reported resistance (2000-5000Ω) for lightning current can be resisted by calloused dry hand that have more than 100,000Ω with internal body resistance of 300Ω, suggesting low incidence of human killings by lightening current. But the total body resistance in water 300Ω and voltage (30V) can kill human [7]. The estimated power of lightening is between 10,000 and 200,000 A with estimated voltage of 20 million to 1 billion V [15]. The resistance to lightening current is from 25-1000 ohms on sweaty palm to 1million ohms on dry calloused hand [2]. Lightening figure is a fractal positive electrical discharge reported in 30% of cases [16]. Using the above formula to calculate the resistance (2x103-5x103Ω) developed by human against lightning, current (104 - 2x107A) and voltage (2x107 - 1x109V) [7] denotes that there is need for high resistance against the effects of lightning current and voltage [19], since lightning had caused 45 fatalities and unusual otolaryngitis [20,21]. But the lethality depends on frequencies of thunderstorm sounds and energies [22].
Conclusion
The LD50 of electric current is very low suggesting high level of toxicity. But because of high resistance shown to the current by human being, the incidence of killing by the current is low.
References
- Nguyen BH, Mackay M, Bailey B, Klassen TP (2004) Epidemiology of electrical and lightning related deaths and injuries among Canadian children and youth. Injury and prevention 10: 122-124.
- Cankaya H, Egeli E, Euliyaoghu Z (2002) Hearing loss caused by lightning strike: case report and review of the literature. J Otolayngol 31(3): 181-183.
- Celikoz B, Isik S, Turegun M, Selmanpakoglu N (1996) An unusual case of lightning strike: full thickness burns of the cranial bones. Burns 22(5): 417-419.
- Cooper MA (1995) Myths, miracles and mirages. Lightening Injury Facts, pp. 1-11.
- Courtman SP, Wilson PM, Mok Q (2003) Case report of a 13-year old struck by lightning. Paediatr Anaesth 13(1): 76-79.
- Dalziel CF (1972) Effects of electrical shock on man. IEEE Spectr 9(2): 41-50.
- Fish RM, Geddes LA (2009) Conduction of electrical current to and through the human body: a review. Open Access J Plastic Surg 9: 407-421.
- Forth G (1984) Animals witches and wind: eastern Indonesian variations on the thunder complex. Anthropos 1984(84): 89-106.
- Gibbs NF, Keel DM (2003) Burns from out of the blue lightning strike: Postgrad Med 2003; 113: 67-68. report and review of fee literature J Dtutaryagol 21: 181-183.
- Kelley MC, Garstand M (2013) On the possible detection of lightning storm by elephants. Animals 3(2): 349-355.
- Lee RC, Cravalho EG, Burke JF (1992) Electrical Trauma, Cambridge University Press, England.
- Lichtenberg R, Dries D, Ward K, Marshal W, Scancon P (1993) Cardiopvascular effects of lightning strikes. J Am Col Cardiol 21(2): 531-536.
- Lifschultz BD, Donoghue ER (1993) Deaths caused by lightning. J Forensic Sci 38(2): 353-358.
- National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) (2009), Worker deaths by electrocution. NIOSH publication No. 98-131.
- Norman ME, Albertson D, Younge BR (2001) Ophthalmic manifestations of lightning strike. Surv Ophthalmol 46(1): 19-24.
- Resink BI, Wetli CV (1996) Lichtenberg figures. Am J forensic Med Pathol 17(2): 99-102.
- Saganuwan SA (2014) Arithmetic method of rough estimation of median lethal dose (LD50) using up-and-down procedure. Toxicol Lett 229: s127
- Seidl S (2005) Pathological features of death from lightning strike. Forensic pathol Rev 4: 3-23.
- Smooth AW, Bentel CA (1964) Electric shock hazard of underwater swimming pool lighting fixtures. IEEE Irans Power Apparent System 83(9): 945-964.
- Wetli CV (1996) Keraunopathology. An analysis of 45 Fatalities. Am J Forensic Med Pathol 17: 89-98.
- Todd DH, Meyers A (1994) An unusual otolaryngologic manifestation of lightning strike. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 110(1): 126-130.
- Saganuwan SA (2018) The lethal frequencies of thunderstorm sound and energies: a mini review. Curr Trend Biomed Engineer 17(1): 1-2.
What Is a Lethal Level of Electrical Voltage
Source: https://juniperpublishers.com/ctbeb/CTBEB.MS.ID.556018.php
0 Response to "What Is a Lethal Level of Electrical Voltage"
Post a Comment